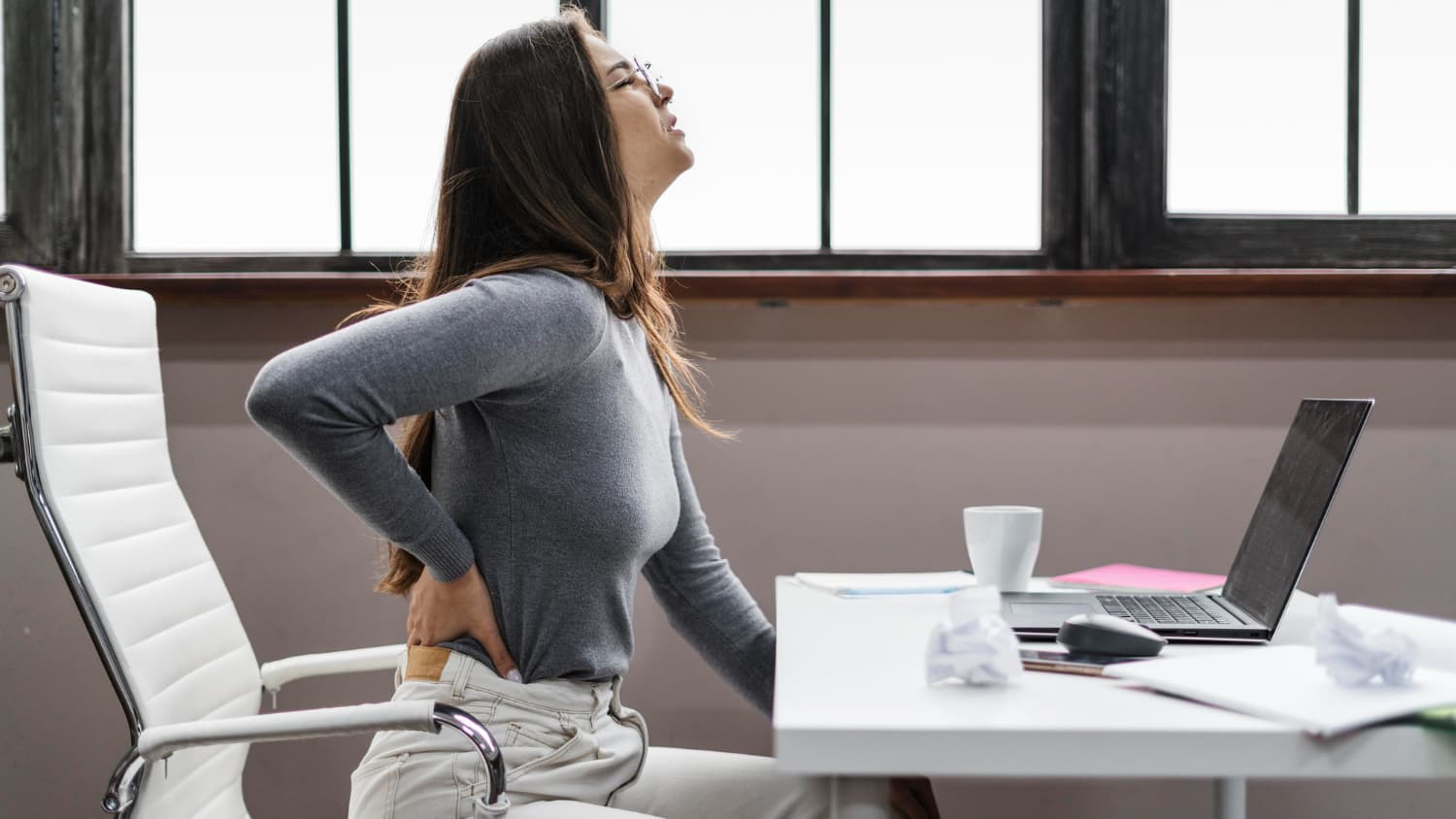
Back spasms are a common problem that can cause discomfort, restrict movement, and even lead to severe pain if left untreated. They occur when the muscles in the back tighten and contract suddenly, often due to injury, overuse, or even nerve problems. These spasms may also be caused by spinal issues or dehydration. Knowing the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for managing back spasms effectively.
Common Causes of Back Spasms
Back spasms can occur due to a variety of reasons. Understanding these causes can help you avoid future issues and find the right treatment.
Muscle Overuse and Strain
One of the most common causes of back spasms is muscle strain. This often happens when you lift something heavy or do intense physical activity without proper form. Overusing your muscles during exercise or work can also cause strain. Bad posture, like sitting hunched over at a desk for long periods, can put extra pressure on your back muscles, leading to spasms.
Dehydration and Electrolyte Imbalance
Your muscles need proper hydration and minerals to work correctly. When you do not drink enough water or have low levels of minerals like potassium, calcium, or magnesium, your muscles are more likely to cramp. This imbalance can trigger back spasms, especially during physical activities or in hot weather when the body loses water quickly.
Herniated Disc or Spinal Issues
Problems in your spine, such as a herniated disc, can also lead to back spasms. A herniated disc occurs when the soft tissue between the bones in your spine slips out of place. This can press on nearby nerves, causing pain and muscle spasms. Other spinal issues, like arthritis, can also irritate the muscles in your back, leading to spasms.
Other Contributing Factors
Several other factors can cause back spasms. Stress is one of them. When you are stressed, your muscles tend to tense up, which can cause spasms. Lack of regular exercise can also weaken your back muscles, making them more prone to spasms. Finally, skipping warm-ups before physical activity can cause your muscles to become tight and spasm.
Symptoms of Back Spasms

Symptoms of Back Spasms
Recognizing the symptoms of back spasms is important for early treatment. Some people may feel a sudden sharp pain, while others may notice ongoing discomfort.
Sudden, Sharp Pain
A sudden and sharp pain in the lower or upper back is one of the first signs of a spasm. This pain may last for a few seconds or minutes, but it can also come and go over several hours. The intensity of the pain depends on how severe the spasm is.
Difficulty Moving
Back spasms can make it hard to move. You may find it difficult to bend over, twist, or even walk. The stiffness in your back limits your range of motion, making even simple movements painful and slow.
Muscle Tightness
You might also feel tightness or a knot in your back. This can happen because the muscles are contracting too much. The area may feel hard to the touch, and the tightness can last for several hours or days, depending on the cause.
Diagnosing Back Spasms
To properly treat back spasms, it is essential to get the right diagnosis. This can help determine if your back pain is caused by muscle issues or something more serious, like spinal problems.
Physical Examination
Your doctor will start by doing a physical exam. This will involve checking your range of motion and pressing on different areas of your back to find where the pain is coming from. They may also ask you to perform certain movements to see how your muscles react.
Imaging Tests
If the doctor suspects a more serious issue, they may suggest imaging tests like X-rays or an MRI. These tests can help identify any problems with the bones or nerves in your spine that may be causing the spasms.
Effective Treatments for Back Spasms

Effective Treatments for Back Spasms
There are several treatment options available for back spasms, ranging from home remedies to professional medical help. The goal of treatment is to relieve pain, relax the muscles, and prevent future spasms.
Rest and Immobilization
Resting is one of the first things you should do when a spasm occurs. Lying down or sitting in a comfortable position helps reduce pressure on your back muscles. However, it is important not to rest for too long because this can make your muscles weaker.
Applying Heat or Cold Therapy
Using ice packs or heating pads can also help. Ice reduces swelling and numbs the area, while heat improves blood flow and relaxes tight muscles. Apply ice for the first 48 hours after a spasm, then switch to heat.
Gentle Stretches and Exercises
Once the pain subsides, doing gentle stretches and exercises can help loosen up your back muscles. Stretching the lower back and hamstrings can reduce tension and prevent future spasms. Exercises that strengthen the core muscles are also helpful for long-term prevention.
Pain Relievers and Muscle Relaxants
Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help ease the pain from spasms. In more severe cases, a doctor might prescribe muscle relaxants to relieve tightness in the muscles.
Physical Therapy
If back spasms are a recurring problem, physical therapy may be needed. A physical therapist can create a personalized exercise program to strengthen your back muscles and improve posture. This can prevent spasms from happening in the future.
When to See a Doctor
In some cases, back spasms can be a sign of a more serious issue. If you experience severe pain that does not go away with rest, or if the spasms are accompanied by numbness or weakness in your legs, it is important to see a doctor right away.
Preventing Future Back Spasms
Prevention is always better than cure, and there are several ways to reduce the chances of getting back spasms in the future.
Proper Posture and Ergonomics
One of the best ways to prevent back spasms is to maintain good posture. Whether you are sitting at a desk or lifting something heavy, make sure your back is aligned properly. Ergonomic chairs, desks, and lifting techniques can help you avoid straining your back muscles.
Regular Exercise and Stretching
Regular physical activity keeps your muscles strong and flexible. Focus on exercises that strengthen your core and lower back. Stretching before and after physical activity can also help prevent spasms by keeping your muscles loose.
Staying Hydrated
Make sure to drink plenty of water throughout the day, especially if you are exercising. This will keep your muscles hydrated and prevent cramping. Eating foods rich in potassium, magnesium, and calcium can also help maintain healthy muscles.
Gradual Warm-up Before Activities
Always warm up your muscles before doing any strenuous physical activities. A proper warm-up prepares your muscles for the activity ahead and reduces the risk of sudden strains or spasms.
Final Thoughts on Managing Back Spasms
Back spasms can be painful and disruptive, but they are manageable with the right approach. Understanding the causes and symptoms of spasms, getting proper treatment, and taking preventive measures can help reduce the frequency and severity of spasms. By staying active, maintaining good posture, and keeping your muscles healthy, you can minimize the chances of future back spasms and maintain a pain-free lifestyle.
For expert advice on managing back pain, visit Physical Therapy Info. If you’re seeking a qualified physical therapist in your area, explore our listing page for local professionals.
James Foster, PT is a licensed physical therapist with over 11 years of hands-on experience in helping individuals improve mobility and live pain-free. As a health writer, James shares expert advice, rehabilitation strategies, and wellness tips to empower readers toward healthier, stronger lives.