Have you ever felt stuck in a loop of negative thoughts, where no matter what you do, you can’t seem to break free? What if the key to changing your life lies in understanding how your thoughts shape your emotions and behaviors? This is the foundation of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), one of the most effective and widely used forms of psychotherapy. In this article, we’ll explore the core principle of CBT, how it works, and why it’s so powerful in helping people overcome challenges like anxiety, depression, and stress.
Key Takeaways
- CBT’s Core Principle: Thoughts, emotions, and behaviors are deeply connected. Changing one can positively influence the others.
- How It Works: CBT helps you identify and replace negative thought patterns with balanced, realistic ones.
- Real-Life Applications: CBT is effective for anxiety, depression, and stress, offering practical tools for daily challenges.
- Benefits: CBT is evidence-based, structured, and focuses on teaching lifelong skills for mental well-being.
- Long-Term Impact: The skills you learn in CBT can improve relationships, reduce stress, and boost confidence long after therapy ends.
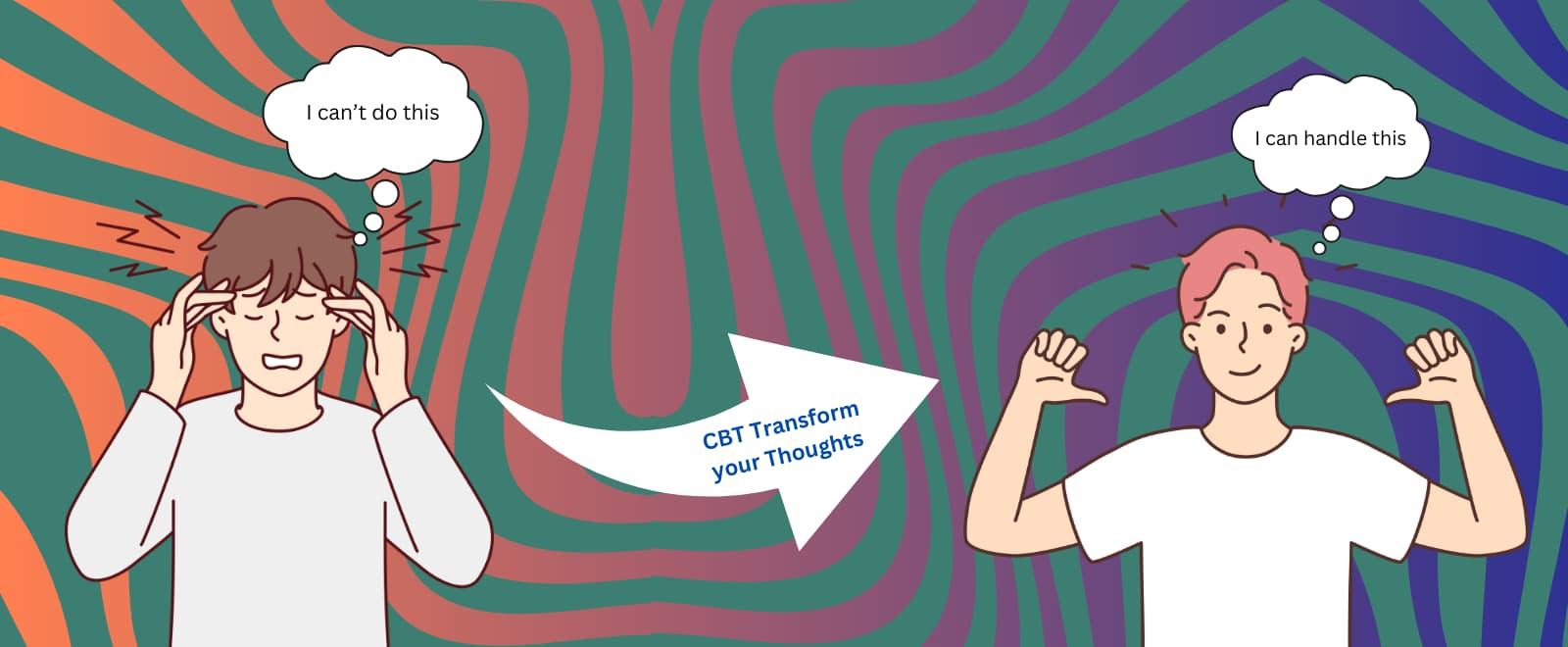
What is the Core Principle of CBT?
At its heart, CBT is based on a simple yet profound idea: our thoughts, emotions, and behaviors are deeply interconnected. This means that the way we think about a situation directly influences how we feel and act. For example:
- If you think, “I’m going to fail this exam,” you might feel anxious and avoid studying.
- If you think, “I can handle this challenge,” you’re more likely to feel confident and take positive action.
CBT helps you identify and challenge unhelpful thought patterns, replacing them with more realistic and balanced ones. By doing so, you can break free from negative cycles and take control of your mental well-being.
How Does CBT Work?
CBT is a structured, goal-oriented therapy that focuses on the present rather than delving deeply into the past. Here’s how it works:
1. Identifying Automatic Thoughts
Automatic thoughts are the immediate, often unconscious thoughts that pop into your mind throughout the day. While some are neutral or positive, others can be negative and distorted. For instance:
- “I’m not good enough.”
- “Everything always goes wrong for me.”
CBT teaches you to recognize these thoughts and question their validity.
2. Challenging Cognitive Distortions
Cognitive distortions are irrational thought patterns that skew your perception of reality. Common examples include:
- Catastrophizing: Assuming the worst will happen.
- Black-and-White Thinking: Seeing things as all good or all bad.
- Overgeneralization: Believing that one negative event means everything will go wrong.
Through CBT, you learn to challenge these distortions and replace them with more balanced thoughts.
3. Behavioral Activation
CBT also emphasizes the role of behavior in shaping emotions. By engaging in positive activities—even when you don’t feel like it—you can improve your mood and break the cycle of negativity. For example, if you’re feeling depressed, scheduling a walk with a friend or pursuing a hobby can help lift your spirits.
Real-Life Applications of CBT
CBT isn’t just a theoretical concept—it’s a practical tool that can be applied to everyday life. Here are some examples:
- Anxiety: A person with social anxiety might learn to challenge thoughts like, “Everyone is judging me,” and replace them with, “I am capable and prepared.”
- Depression: Someone struggling with depression might use behavioral activation to gradually reintroduce enjoyable activities into their routine.
- Stress Management: CBT techniques like cognitive restructuring can help you reframe stressful situations and develop healthier coping mechanisms.
CBT is highly effective for managing anxiety, but it can be even more powerful when combined with other techniques like somatic exercises. These exercises focus on the mind-body connection, helping you release physical tension and calm your nervous system. Learn more about somatic exercises for anxiety and how they can enhance your mental well-being.
The Benefits of CBT
CBT is backed by decades of research and has been proven effective for a wide range of mental health conditions. Here are some of its key benefits:
- Evidence-Based: CBT is supported by extensive scientific research.
- Practical Skills: It equips you with tools you can use long after therapy ends.
- Short-Term and Focused: CBT is typically a short-term therapy with clear goals.
- Versatile: It can be adapted to treat various conditions, from anxiety and depression to PTSD and OCD.
CBT is one of the most effective treatments for anxiety disorders, with studies showing a 60-80% improvement rate in patients (source: APA). If you’re interested in trying CBT techniques, check out these free CBT worksheets to get started. Whether you’re dealing with anxiety, depression, or stress, CBT offers practical tools to help you take control of your mental health.
What to Expect in CBT Sessions
If you’re considering CBT, here’s what you can expect:
- Assessment: Your therapist will gather information about your concerns and goals.
- Psychoeducation: You’ll learn about the connection between thoughts, emotions, and behaviors.
- Skill-Building: You’ll practice techniques like cognitive restructuring and behavioral activation.
- Homework: You may be given assignments to practice skills between sessions.
- Progress Tracking: Your therapist will help you monitor your progress and adjust the treatment plan as needed.
Long-Term Impact of CBT
One of the most powerful aspects of CBT is that it teaches you skills you can use for life. By learning to identify and challenge negative thoughts, manage your emotions, and engage in positive behaviors, you can build resilience and improve your overall well-being. These skills can also enhance other areas of your life, such as:
- Relationships: Better communication and conflict resolution.
- Work Performance: Increased confidence and productivity.
- Self-Esteem: A more positive self-image.
Take the First Step Toward a Healthier Mind
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy is more than just a treatment—it’s a pathway to understanding yourself and taking control of your mental health. By learning to reframe your thoughts and behaviors, you can break free from negative cycles and create a more fulfilling life.
If you’re ready to explore how CBT can help you, reach out to a qualified therapist today. Remember, the first step is often the hardest, but it’s also the most important. You deserve to live a life free from the weight of negative thoughts—and CBT can help you get there.
James Foster, PT is a licensed physical therapist with over 11 years of hands-on experience in helping individuals improve mobility and live pain-free. As a health writer, James shares expert advice, rehabilitation strategies, and wellness tips to empower readers toward healthier, stronger lives.